Precision Turned Parts for Your Custom Machining Projects
Introduction
Precision turned parts are an essential component of custom machining projects. These parts are manufactured to meet strict tolerances and specifications, ensuring accuracy, reliability, and consistency in the final product. They can be produced in various materials, including metals, plastics, and composites, and they have a wide range of applications in industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical, and electronics.
Customized Cnc Turning Plastic Parts
Understanding Precision Turned Parts
Precision turned parts are components that have been manufactured using a precision machining process called turning. Precision turning machining involves rotating a bar of material against a cutting tool to remove material and create a desired shape. The cutting tool moves along the bar in a linear or rotating motion, creating the desired shape with high precision and accuracy.
Precision turned parts can be produced in various shapes, sizes, and materials, including metals, plastics, and composites. Some common types include:
- Shafts: cylindrical components used for transmitting power in machines and equipment.
- Bushings: cylindrical components used for reducing friction between two moving parts.
- Pins: cylindrical components used for fastening or aligning parts.
- Connectors: components used for connecting different parts in a system.
- Valves: components used for regulating the flow of fluids or gases in a system.
The advantages of using precision turned parts in custom machining projects are numerous. Some of the key advantages include:
- Precision and accuracy: Precision turned parts are manufactured with high precision and accuracy, meeting strict tolerances and specifications. This ensures that the final product is reliable, consistent, and performs as intended.
- Cost-effective: Precision turning is a cost-effective manufacturing process, allowing for the production of high-quality parts at a lower cost compared to other manufacturing processes.
- Versatility: Precision turned parts can be produced in various shapes, sizes, and materials, making them versatile and suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Faster lead times: Precision turning can produce parts quickly, reducing lead times and allowing for faster production cycles.
- Reduced waste: Precision turning produces less waste compared to other manufacturing processes, reducing material costs and minimizing environmental impact.
Materials Used in Precision Turning
Precision turned parts can be manufactured using a wide range of materials, each with its unique properties and advantages. The choice of material depends on the specific application and the required properties of the final product. In this section, we will provide an overview of the different materials commonly used in precision turning, their properties, their suitability for different applications, and a comparison of their cost and performance.
Metals
Metals are the most commonly used material in precision turning. They have excellent strength, durability, and thermal conductivity, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. Some of the most commonly used metals in precision turning include:
- Aluminum: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has excellent thermal conductivity. It is commonly used in the aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries.
- Steel: Steel is strong, durable, and has excellent wear resistance. It is commonly used in the automotive, aerospace, and industrial industries.
- Stainless steel: Stainless steel is corrosion-resistant and has excellent strength and durability. It is commonly used in the medical, food processing, and chemical industries.
- Titanium: Titanium is lightweight, strong, and has excellent corrosion resistance. It is commonly used in the aerospace, medical, and automotive industries.
- Brass: Brass is corrosion-resistant and has excellent electrical conductivity. It is commonly used in the electronics and plumbing industries.
The choice of metal depends on the specific application and the required properties of the final product. For example, aluminum is commonly used in the aerospace industry because of its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties, while stainless steel is commonly used in the medical industry because of its corrosion resistance and biocompatibility.
In terms of cost and performance, metals vary widely. Aluminum is relatively inexpensive compared to other metals, while titanium is more expensive. Steel and stainless steel are in the mid-range in terms of cost. Performance-wise, titanium has the highest strength-to-weight ratio, while steel has excellent wear resistance.
Plastics
Plastics are another common material used in precision turning. They have excellent chemical resistance, low friction, and are lightweight. Some of the most commonly used plastics in precision turning include:
- Acetal: Acetal is a thermoplastic with excellent strength, stiffness, and wear resistance. It is commonly used in the automotive and industrial industries.
- Nylon: Nylon is a thermoplastic with excellent strength, toughness, and wear resistance. It is commonly used in the automotive, industrial, and consumer goods industries.
- PEEK: PEEK is a thermoplastic with excellent chemical resistance, high temperature resistance, and wear resistance. It is commonly used in the aerospace, medical, and industrial industries.
- Polycarbonate: Polycarbonate is a thermoplastic with excellent impact resistance and clarity. It is commonly used in the electronics and automotive industries.
The choice of plastic depends on the specific application and the required properties of the final product. For example, PEEK is commonly used in the aerospace industry because of its high temperature resistance and chemical resistance, while polycarbonate is commonly used in the electronics industry because of its clarity and impact resistance.
In terms of cost and performance, plastics are generally less expensive than metals. Acetal and nylon are relatively inexpensive, while PEEK and polycarbonate are more expensive. Performance-wise, PEEK has excellent chemical resistance and high-temperature resistance, while polycarbonate has excellent impact resistance and clarity.
Composites
Composites are a combination of two or more materials with different properties, resulting in a material that has superior properties compared to its individual components. Composites are commonly used in precision turning for their high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance. Some of the most commonly used composites in precision turning include:
- Carbon fiber: Carbon fiber is a composite material with excellent strength and stiffness. It is commonly used in the aerospace, automotive, and sports industries.
- Fiberglass: Fiberglass is a composite material with excellent strength, stiffness, and corrosion resistance. It is commonly used in the marine, automotive, and construction industries.
- Kevlar: Kevlar is a composite material with excellent strength and impact resistance. It is commonly used in the aerospace, military, and industrial industries.
Cnc Turning Machining
Precision Turning Techniques
Precision turning is a versatile machining process that can produce complex and precise shapes with high accuracy and repeatability. In this section, we will provide an explanation of the different precision turning techniques used in custom machining projects, their advantages and disadvantages, and a comparison of their cost and lead time.
CNC Turning
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) turning is a precision turning technique that uses computerized control to operate the cutting tool. CNC turning allows for the production of complex shapes with high precision and accuracy. The advantages of CNC turning include:
- High precision and accuracy: CNC turning machines can produce parts with high precision and accuracy, meeting strict tolerances and specifications.
- Versatility: CNC turning machines can produce a wide range of shapes and sizes, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Automation: CNC turning machines are automated, reducing the need for manual labor and increasing efficiency.
The disadvantages of CNC turning include:
- Cost: CNC turning machines are expensive to purchase and maintain, making them less suitable for small-scale production.
- Setup time: CNC turning machines require setup time, which can increase lead times.
In terms of cost and lead time, CNC turning is generally more expensive and has longer lead times compared to other precision turning techniques.
Swiss Turning
Swiss turning is a precision turning technique that is ideal for producing small, complex parts. Swiss turning involves rotating a bar of material while simultaneously moving the cutting tool along the bar, creating precise shapes with high accuracy. The advantages of Swiss turning include:
- High precision and accuracy: Swiss turning machines can produce parts with high precision and accuracy, meeting strict tolerances and specifications.
- Suitable for small parts: Swiss turning is ideal for producing small, complex parts with high precision and accuracy.
- Reduced setup time: Swiss turning machines require less setup time compared to CNC turning machines, reducing lead times.
The disadvantages of Swiss turning include:
- Limited flexibility: Swiss turning machines are less versatile compared to CNC turning machines, limiting their range of applications.
- Higher cost for large parts: Swiss turning machines may not be cost-effective for producing large parts due to the high cost of material and setup time.
In terms of cost and lead time, Swiss turning is generally less expensive and has shorter lead times compared to CNC turning for small, complex parts.
Centerless Grinding
Centerless grinding is a precision turning technique that involves grinding a cylindrical workpiece without the use of a center. Centerless grinding is ideal for producing parts with a high surface finish and tight tolerances. The advantages of centerless grinding include:
- High surface finish: Centerless grinding can produce parts with a smooth surface finish and tight tolerances.
- Suitable for long and thin parts: Centerless grinding is ideal for producing long and thin parts with high precision and accuracy.
- Reduced setup time: Centerless grinding machines require less setup time compared to other precision turning techniques, reducing lead times.
The disadvantages of centerless grinding include:
- Limited versatility: Centerless grinding is limited to cylindrical parts and may not be suitable for producing complex shapes.
- Higher cost for short runs: Centerless grinding machines may not be cost-effective for short production runs due to the high cost of setup time.
In terms of cost and lead time, centerless grinding is generally less expensive and has shorter lead times compared to CNC turning and Swiss turning for long and thin parts.
Honing
Honing is a precision turning technique that involves removing material from the inside surface of a cylindrical part to improve its surface finish and accuracy. Honing is ideal for producing parts with a high surface finish and tight tolerances. The advantages of honing include:
- High surface finish: Honing can produce parts with a smooth surface finish and tight tolerances.
- Suitable for internal surfaces: Honing is ideal for producing parts with precise internal surfaces.
- Reduced setup time: Honing machines require less setup time compared to other precision turning techniques, reducing lead times.
The disadvantages of honing include:
- Limited versatility: Honing is limited to cylindrical parts and may not be suitable for producing complex shapes.
- Higher cost for short runs: Honing machines may not be cost-effective for short production runs due to the high cost of setup time.
In terms of cost and lead time, honing is generally less expensive and has shorter lead times compared to CNC turning and Swiss turning for internal surfaces.
In summary, precision turning techniques include CNC turning,Swiss turning, centerless grinding, and honing. Each technique offers unique advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of technique depends on the specific application and the required properties of the final product. CNC turning offers high precision and versatility but is more expensive and has longer lead times. Swiss turning is ideal for producing small, complex parts but is less versatile and may not be cost-effective for large parts. Centerless grinding is ideal for producing parts with a high surface finish but is limited to cylindrical parts. Honing is ideal for producing parts with precise internal surfaces but is also limited to cylindrical parts. When selecting a precision turning technique, it is important to consider both the cost and lead time, as well as the specific requirements of the final product.
Choosing the Right Manufacturer for Precision Turned Parts
Choosing the right manufacturer for precision turned parts is crucial to ensuring that the final product meets the desired specifications. A reliable manufacturer will have the necessary expertise, experience, and equipment to produce high-quality precision turned parts that meet strict tolerances and specifications.
Importance of Choosing the Right Manufacturer
Choosing the right manufacturer for precision turned parts is important for several reasons. First, a reliable manufacturer will have the necessary expertise and experience to produce high-quality parts that meet strict tolerances and specifications. Second, a reliable manufacturer will use high-quality materials and equipment, ensuring that the final product is durable and reliable. Third, a reliable manufacturer will have a quality control process in place to ensure that each part meets the desired specifications. Finally, a reliable manufacturer will have efficient production processes and lead times, ensuring that the final product is delivered on time and within budget.
Tips for Selecting the Right Manufacturer
When selecting a manufacturer for precision turned parts, it is important to consider several factors. Here are some tips for selecting the right manufacturer:
- Look for a manufacturer with experience in precision turning: Choose a manufacturer with experience and expertise in precision turning to ensure that the final product meets the desired specifications.
- Check the manufacturer’s certifications: Look for a manufacturer that has industry certifications, such as ISO 9001, which ensures that the manufacturer has a quality management system in place.
- Review the manufacturer’s equipment and facilities: Ensure that the manufacturer has modern and well-maintained equipment and facilities to produce high-quality precision turned parts.
- Consider the manufacturer’s materials and sourcing: Choose a manufacturer that uses high-quality materials and has a reliable supply chain to ensure that the final product is durable and reliable.
- Check the manufacturer’s quality control process: Look for a manufacturer that has a robust quality control process in place to ensure that each part meets the desired specifications.
- Review the manufacturer’s production processes and lead times: Choose a manufacturer that has efficient production processes and lead times to ensure that the final product is delivered on time and within budget.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Manufacturer
When selecting a manufacturer for precision turned parts, here are some factors to consider:
- Expertise and experience in precision turning
- Industry certifications and quality management systems
- Equipment and facilities
- Materials and sourcing
- Quality control process
- Production processes and lead times
- Customer service and communication
In summary, choosing the right manufacturer for precision turned parts is crucial to ensuring that the final product meets the desired specifications. When selecting a manufacturer, it is important to consider factors such as expertise and experience, industry certifications, equipment and facilities, materials and sourcing, quality control processes, production processes and lead times, and customer service and communication. By following the tips outlined above and carefully considering these factors, you can select a reliable and experienced manufacturer that will produce high-quality precision turned parts that meet your specific requirements.
Ziss Contura Three Coordinate Detection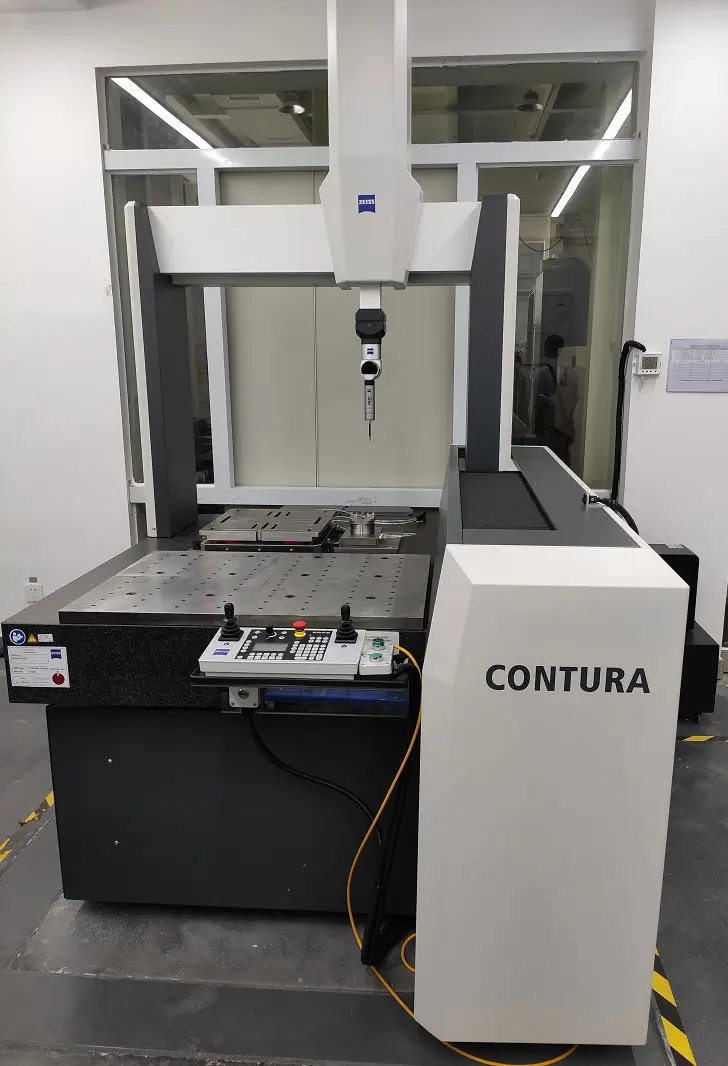
Quality Control in Precision Turning
Quality control is a critical aspect of precision turning that ensures that the final product meets the desired specifications and requirements. Quality control measures are used throughout the custom machining process to monitor and maintain the quality of the parts produced. In this section, we will provide an explanation of the importance of quality control in precision turning, an overview of the different quality control measures used in custom machining projects, and a comparison of different quality control standards and certifications.
Importance of Quality Control
Quality control is essential in precision turning for several reasons. First, it ensures that the final product meets the desired specifications and requirements, ensuring that the parts are functional, durable, and reliable. Second, it helps identify and address any issues or defects in the production process, improving the overall quality of the parts produced. Third, it helps maintain consistency and repeatability in the production process, ensuring that each part produced is of the same high quality.
Quality Control Measures in Precision Turning
Several quality control measures are used in precision turning to ensure that the final product meets the desired specifications and requirements. These measures include:
- Inspection and measurement: Inspection and measurement are used to ensure that each part produced meets the desired specifications and requirements. This includes using tools such as micrometers, calipers, and gauges to measure the dimensions and tolerances of the parts produced.
- Statistical process control: Statistical process control is used to monitor and control the production process, ensuring that each part produced is consistent and within the desired specifications. This includes using statistical methods to analyze data and identify any trends or patterns that may indicate issues or defects in the production process.
- Non-destructive testing: Non-destructive testing is used to detect any defects or flaws in the parts produced without damaging or destroying them. This includes methods such as x-ray and ultrasonic testing.
- Documentation and traceability: Documentation and traceability are used to ensure that each part produced can be traced back to its production process and materials. This includes maintaining detailed records of the production process and materials used, as well as using unique identifiers to track each part produced.
- Quality management systems: Quality management systems are used to ensure that the production process meets the desired quality standards and requirements. This includes implementing processes and procedures to monitor and control the production process and ensuring that all personnel involved in the production process are trained and qualified to perform their roles.
Quality Control Standards and Certifications
Several quality control standards and certifications are used in precision turning to ensure that the final product meets the desired quality standards and requirements. These include:
- ISO 9001: ISO 9001 is a quality management system standard that sets out the requirements for a quality management system. This standard is widely recognized and used in various industries to ensure that the production process meets the desired quality standards and requirements.
- AS9100: AS9100 is a quality management system standard that is specifically designed for the aerospace industry. This standard sets out the requirements for a quality management system that meets the specific needs and requirements of the aerospace industry.
- NADCAP: NADCAP is a global accreditation program that is used in the aerospace and defense industries to ensure that suppliers meet the specific quality standards and requirements of these industries.
- RoHS: RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) is a directive that restricts the use of hazardous substances in the production of electrical and electronic equipment. This directive is widely recognized and used in various industries to ensure that the final product is safe and environmentally friendly.
- REACH: REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) is a regulation that aims to improve the protection of human health and the environment from the risks that can be posed by chemicals. This regulation is widely recognized and used in various industries to ensure that the final product is safe and environmentally friendly.
In summary, quality control is a critical aspect of precision turning that ensures that the final product meets the desired specifications and requirements. Quality control measures such as inspection and measurement, statistical process control, non-destructive testing, documentation and traceability, and quality management systems are used throughout the custom machining process to monitor and maintain the quality of the parts produced. Quality control standards and certifications such as ISO 9001, AS9100, NADCAP, RoHS, and REACH are used to ensure that the final product meets the desired quality standards and requirements of specific industries. By implementing robust quality control measures and adhering to quality control standards and certifications, manufacturers can ensure that the final product is of high quality, safe, and reliable, meeting the specific needs and requirements of their customers and industries.
Conclusion
Precision turned parts are an essential component of many custom machining projects across a wide range of industries. These parts require a high level of precision and accuracy to ensure that the final product meets the desired specifications and requirements. Companies who are considering custom machining projects, we encourage you to consider the importance of precision turned parts in achieving the desired specifications and requirements of your project. By choosing the right manufacturer and implementing quality control measures, you can ensure that the final product is safe, reliable, and effective.
Contact Us